Table of Contents
Ventilation
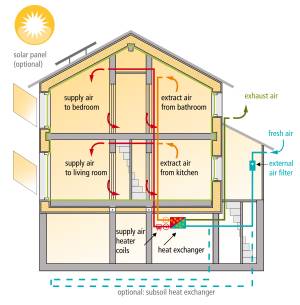
The health and comfort are the most important elements for the Passive House design, the excellent indoor air quality is indispensable. But this can only be achieved if stale air is exchanged with fresh outdoor air at regular intervals. This can definitely not be done by just opening windows twice a day.
Ventilation will work accurately only if stale air is removed constantly from the kitchen, bathrooms, and all other rooms with air pollution. Fresh air has to be supplied to the living room, children’s room, sleeping rooms, and workrooms to substitute the removed air. The system will supply exactly as much fresh air as is needed for comfort and for good indoor air quality; only outdoor air will be supplied – no recirculated air. This will lead to a high level of indoor air quality. Read more about:
- Webinar: Ventilation Systems and Technologies
- Window ventilation: Passive House - 6 reasons why you still need opening windows
- Ventilation in Summer: Importance of summer ventilation in Passive House buildings
Ventilation Units
The ventilation units provide clean, pollen-free and dust-free air while eliminating excess moisture and odours. In the winter,the fresh supply air is preheated and can thus be brought into the building at a temperature of 16°C and the heat can remain in the building. On hot summer days, on the other hand, the supply air is cooled (almost) to room air temperature by the heat recovery. The high-quality ventilation unit ensures that the supply and exhaust air ducts in the heat exchanger are leak proof, so that fresh and used air is never mixed. The high-quality ventilation unit saves much more energy through the prevention of heat losses than they use to run. Check Component certificate criteria and certified ventilation units to see all the high-efficient components.
Air flow rate
The appropriate air flow rate in the ventilation system is to ensure the proper functioning of the system and to achieve comfortable indoor conditions. It is essential that not only the planned volume flow rates are achieved in individual parts or rooms of the building, but also that a balanced mass flow between the exhaust and extract air is ensured. Read her to know how you can control Air volume in the ventilation system.
Design aspects
Planning a ventilation system by yourself is workable, here you learn how you can build ventilation system step by step.
- Tool: Ventilation tools
Ventilation guidance for different building typologies
Ventilation for residential building
Ventilation in non-residential buildings
Ventilation in non-residentail building has been a topic for the Research Group for Cost-effective Passive Houses.
You can find the original publications in German here: Ventilation in Passive House - non-residential buildings
The selected topics are translated into English, you can find them here
Ventilation in for retrofit projects
Ventilation for school commercial kitchen, large hall, hospital and retail stores
See also
Read more about Building Services